Batteries An important solution for energy storage
Large-scale battery energy storage systems (BESS) can handle fluctuations in power supply, shifting renewable energy from times of low demand but high production to those of low production but high demand. These important systems help make the development of additional renewable energy capacity possible, accelerating the transition to a carbon-free energy future.
Axpo's role
Batteries are already an integral part of our everyday lives, from powering our smartphones and laptops to ensuring that our electric cars can get from A to B. And today, large-scale storage systems are making a growing contribution to the stabilisation of our electricity grids.
The ability BESS devices have to quickly store electricity and make it available as and when required means that production and consumption are always balanced.
Axpo combines in-depth knowledge of trading on European energy markets with our many years of experience operating systems and state-of-the-art calculation techniques based on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. This allows us to make make best use of our battery storage systems and enhance the value of our storage portfolio. Axpo identifies the various revenue streams available in each country, optimises operating strategies accordingly, and designs the storage systems. This video shows how a large scale battery storage facility works.

Current projects
Switzerland
Axpo is now expanding its business in its home market. In Gurtnellen (Canton of Uri), Axpo and energieUri are building two large-scale battery storage facilities with a capacity of 50 MW (Axpo) and 8.6 MW (energieUri). The 50 MW facility could store a maximum of 100 megawatt hours. This corresponds to the average annual electricity consumption of 22 four-person households. The storage facilities are scheduled to go into operation in the course of 2026.
Sweden
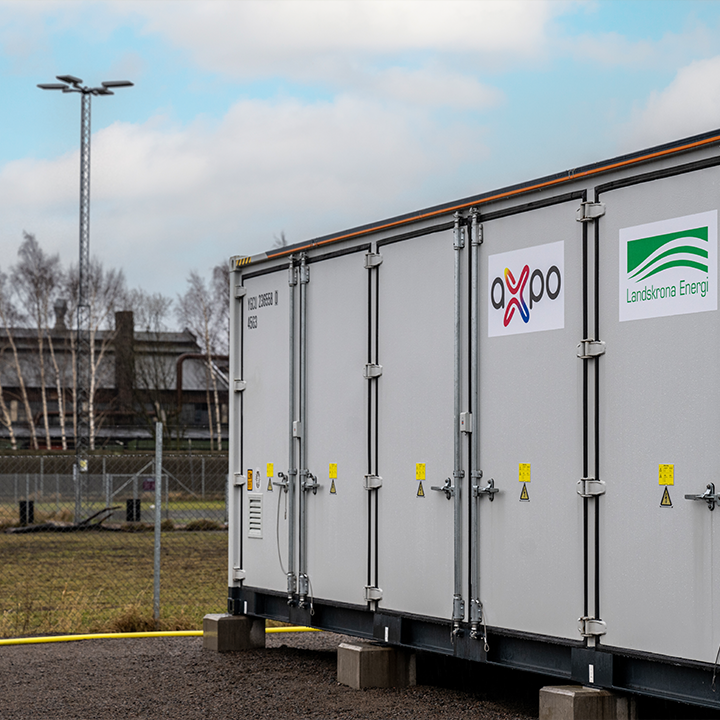
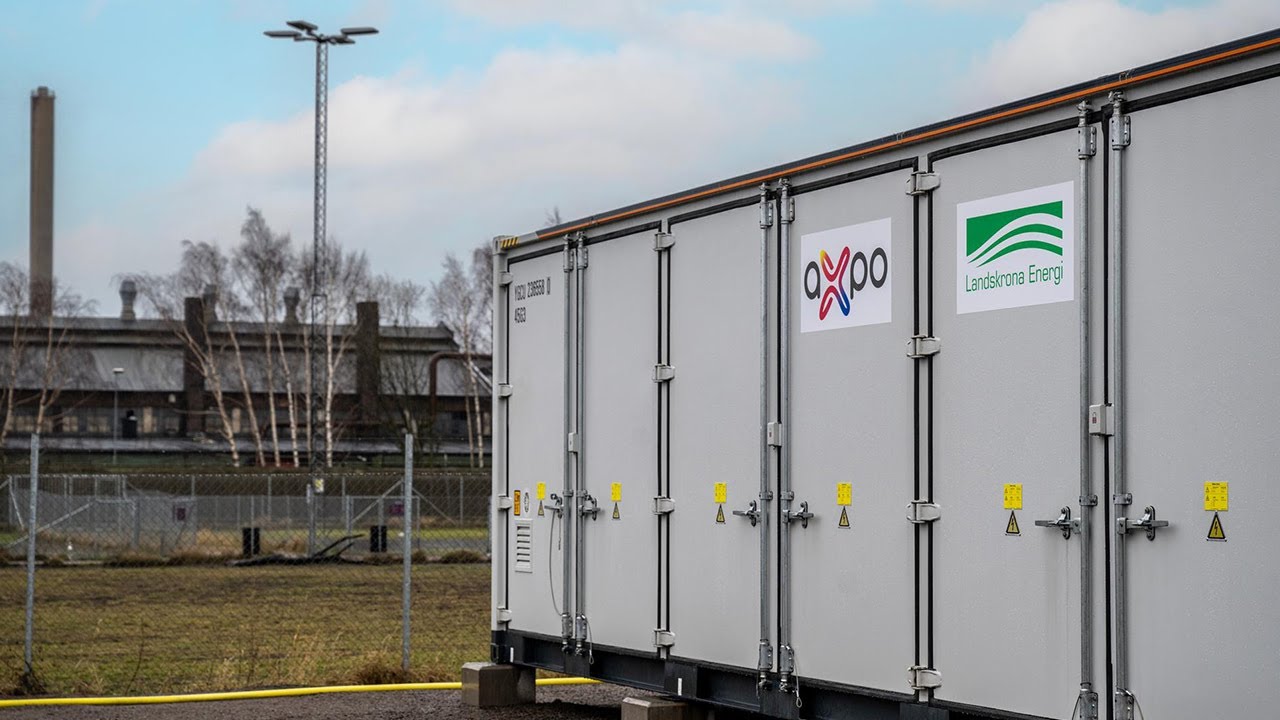
Axpo’s first battery energy storage system in Sweden became operational in February 2024. The 20MW/20MWh lithium-ion based facility was connected to the grid by local energy company Landskrona Energi, and balances electricity supply on the regional grid. The system’s 20 MW is capable of supplying around 4,000 households with electricity for one hour.
The first battery storage components were delivered at the end of September 2023. You can see how the system was constructed in the following videos:
Delivery of the containers for the large battery storage systems in autumn 2023

The construction work on the plant in a time-lapse
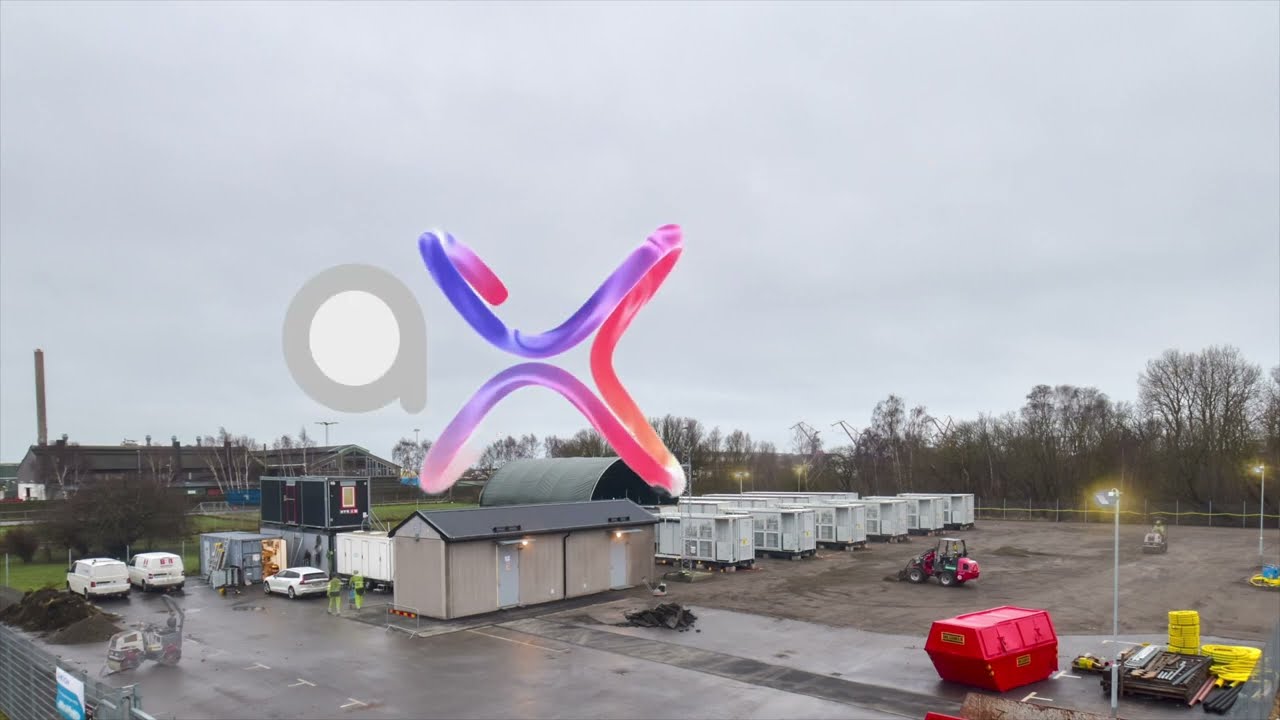

The large battery storage facility, which was officially opened in February 2024
Project development
Axpo has the experience to develop, build, manage and commercially operate renewable energy and large-scale battery storage solutions across Europe.
The most important answers on the topic of batteries
A BESS can be completed in around 12 months and operate for around 20 years. The impact on the environment is minimal during construction while the system’s operation is environmentally friendly.
The majority of battery cells are manufactured in Asia. The alkali metal lithium is the most important battery component of lithium-ion batteries. Most mining of lithium takes place in South America, Australia and China.
A lithium-ion battery’s storage capacity decreases with both time and use. Using one cycle per day, you can expect a reduction in capacity of around 2 per cent a year.
Batteries contain critical raw materials that are rarely found in Europe. When the battery reaches the end of its life, the raw materials can be recycled.
Costs
Due to technological progress and economies of scale, it is reasonable to assume that the investment costs for BESS will decrease over the long term. However, bottlenecks in production capacity or the procurement of raw materials, could temporarily drive up costs.
Regulatory framework conditions
Battery storage systems both consume and produce electricity and are used in many different markets. It is therefore important that clear framework conditions are set for their construction and operation.
Grid conditions
In most countries, transmission and distribution networks were historically designed for the centralised production of electricity. The amount of connected load to be installed depends on the feed-in point and network topology of each specific location.
- A battery’s storage capacity is the amount of energy it can store, measured in megawatt hours ( MWh).
- Power is the energy per unit of time that a battery can charge or discharge, measured in megawatts (MW).
- The C-rate measures how quickly a battery can be charged and discharged. This is calculated by dividing its performance by its storage capacity.
- The state of health (SoH) of a battery is assessed by comparing the storage capacities of a used and a new battery. At the beginning of its life, a battery’s SoH is 100 per cent.
- The state of charge (SoC) indicates the charge level of a battery: at 0 per cent the battery is empty and at 100 per cent it is fully charged.
- The number of cycles indicates how many equivalent full charge-and-discharge cycles a battery performs in a certain period of time. This is usually 1 to 2 equivalent full charge cycles per day.
- Round-trip efficiency measures the energy that can be recovered compared to the energy put into storage (output divided by input). Round-trip efficiency is typically 85 per cent or higher.
- The lifespan of a battery depends on its operation. Frequent charging and discharging as well as extreme charging conditions reduce a battery’s lifespan.
How it works?
What does a battery storage system do (the example of Landskrona project)?
The battery supports grid security. This is necessary because the grid is not always fully utilised. The 20 MW / 20 MWh battery storage system is charged when energy production is high (in the example of the storage facility in Sweden, mainly from wind energy). In turn, it is discharged when less energy is generated.




.jpg)